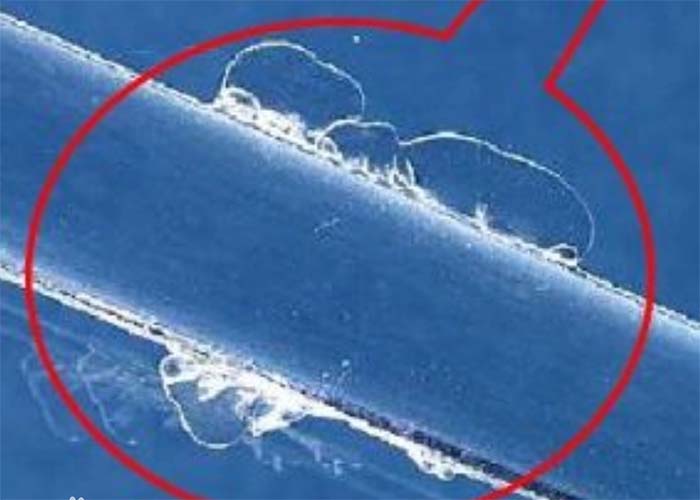
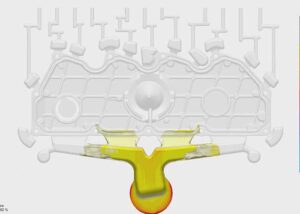
What is a flash injection molding?
Flash, also known as overflow, flare, burr, etc., mostly occurs at the opening and closing positions of the mold, such as the parting surface of the movable mold and the static mold, the sliding part of the slider, the gap of the insert, and the hole of the ejector pin.
In some places, the flash is largely caused by the failure of the mold or the clamping force of the machine. Generally speaking, due to the influence of various factors, it is impossible for plastic parts to never produce flash.
During die forging, the excess metal in the cavity of the final forging die flows into the flash slot to form a circle of metal around the forging. It has the function of ensuring that the metal fills the mold cavity. It must be practical after die forging.
During the molding process, it overflows into the gap between the mold clamping line or the ejector pin and remains on the remaining material edge of the plastic part. It can be removed by polishing, grinding, and other methods. This is due to the low accuracy of the contact surface between the male mold and the female mold, the excessive amount of material, and the leakage of the remaining material at the weak seal.
Causes of flash injection molding
How to reduce flash and improve the quality of plastic parts is an important research topic in the fields of plastic molding processing and precision injection molding. The flash edge may be caused by the following reasons.
1. If the maximum clamping force of the machine is not enough, a machine with sufficient clamping force should be selected.
The hinges of the clamping machine are worn or the sealing elements of the clamping cylinder are worn and the oil drips or backflows, which causes the clamping force to drop. The heating system is out of control and the actual temperature is too high. Check the thermocouple, heating coil problems, etc.
(1) Unbalanced mold cavity distribution or insufficient parallelism causes local flash and local dissatisfaction due to unbalanced forces. The runner should be placed in the center of mass symmetry as far as possible without affecting the integrity of the part.
(2) Unbalanced forces on movable components and sliding cores in the mold will cause flash.
(3) When the mold is poorly exhausted, the air under pressure will expand the parting surface of the mold and cause the flash to appear. A good exhaust system should be set up or an exhaust ditch should be dug on the parting surface.
2. If the fluidity of the plastic is too large, or adds too much lubricant, the pressure, speed, temperature, etc.
Should be appropriately reduced, and the amount of lubricant used should be reduced. If necessary, plastics with low fluidity should be used.
3. Processing and adjustment.
(1) If the set temperature, pressure, and speed are too high, the segmented injection should be used. Injection time, pressure holding time, and too much feed will cause flash.
(2) When adjusting, the hinge of the mold clamping machine is not straight, or the mold adjusting nut often moves when opening or clamping the mold, which causes the clamping force to be insufficient, and flashing occurs.
(3) The parallelism between the adjusting head and the diode is not enough or the pressure of the adjusted system is too high.
4. Reasons for recurring dissatisfaction with flash and parts.
(1) Uneven particle size of the plastic raw materials will cause the amount of the feed to be uncertain.
(2) The over-plastic head, over-apron, and over-rubber washer of the screw are worn too much, so the molten material may slip between the screw and the inside of the barrel and return to cause flashing or dissatisfaction.
(3) The cooling system at the inlet fails, causing the adjustment of the feed.
(4) The set injection volume of the barrel is insufficient, that is, if the cushion is too small, it will cause flashing or part dissatisfaction when the material is shot.
Flash injection molding solution
First of all, the cause of flash.
- The sliding surface of the mold parting surface (PL) does not match;
- The injection pressure is too high;
- The offset of the injection machine;
- Insufficient clamping force.
Related mold issues.
1. The parting surface PL of the mold, sliding mating surface, demolding pins, spacers, etc.
The gaps between the various grooves that constitute the mold will become flash when the material is lost. The flash is a wedge-shaped block. There is a tendency to gradually increase;
2. The principle of removing flash from products is generally to repair the mold.
For flashes that occur temporarily due to poor molding conditions, the barrel temperature should be lowered. Set parameters in the direction of lowering the mold temperature and lowering the injection speed to reduce the fluidity of the material. However, it should be noted that this will cause residual internal stress in the product.
The solution
1. Instantly.
Lower the injection pressure and lower the temperature of the heating barrel. Reduce injection speed;
2. Short-term.
Grind the flashing surface of the mold;
3. Long-term.
The mold uses hard steel material.
Due to the difference in the materials, the material with good fluidity is prone to flash, so the parting surface of the mold must be tight; the viscosity of the crystalline material is very low when it is melted. In particular, the tightness of the mold parting surface is required.
Reference matters
- It should be noted that excessive pressure on the mold will also produce flashing, and foreign objects between the parting surfaces will damage the mold and produce flashing;
- The mold material usually uses materials such as S50C (Japanese JJS standard is equivalent to domestic 50# steel) and pre-hardened special steel of HRC30, so it is difficult to produce flash on the parting surface.
You may also be interested in the below articles.
Summary Of 50 Injection Mold Structure Operation Dynamic Diagrams
Auto Parts Stamping Die Design Concept