After the read, you will learn:
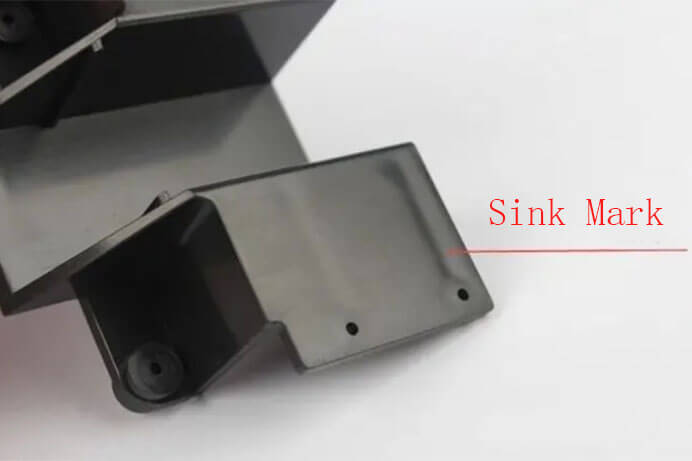
What is the Sink Mark?
What is the sink mark in injection molding?
How do sink marks form?
Why does the sink mark of injection molded parts of products occur?
What are the reasons for the sink mark of the injection molding machines?
What causes the sink mark of injection molded parts?
What is the Sink Mark of injection molded parts?
Definition of Sink Mark: Local collapse of the surface of the molded part (or dimple-like or gully-like).
Sink marks are areas in a molded part where the surface is deformed into a depression. The depressions typically occur in areas of thick geometry and are caused by uneven cooling of the injection material.
What is the sink mark in injection molding?
Sink marks are small craters or depressions that develop in thicker areas of the injection molded prototype when shrinkage occurs in the inner portions of the finished product. The effect is somewhat similar to sinkholes in topography but caused by shrinkage rather than erosion.
How do sink marks form?
Sink marks are caused mainly by thermal contraction (shrinkage) during cooling. After the material on the outside has cooled and solidified, the core material starts to cool. Its shrinkage pulls the surface of the main wall inward, causing a sink mark.
Why does the sink mark of injection molded parts of products occur?
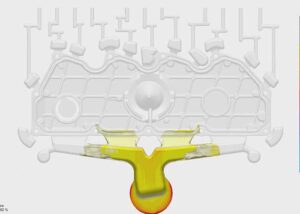
Sink marks of injection molded parts caused by too thick ribs
Rib thick, rib and bottom plate meet thick, where the plastic concentration, cooling, around the rib and plate first curing, this rib, plate meeting place in the center remains liquid, after condensing the plastic in the first curing plastic shrinkage, the plastic around it has the role of inhalation (Sucking-in).
If any of the condensation layers is weaker (generally in the rib opposite the mold surface), the place may collapse into a depression. The thickness of the rib is preferably 50% of the thickness of the base plate, and can even be thinner.
What are the reasons for the sink mark of injection molded parts?
The temperature of the mold surface opposite to the rib is too high, causing shrinkage of the injection molded parts.
The temperature of the mold surface opposite to the rib is higher than that of its vicinity.
Generally speaking, the mold temperature indeed remains high because of the concentration of molten rubber nearby and the large heat load), the condensation layer is thin and not rigid enough, and when the central molten rubber cures, the residual stress may pull the thinner condensation layer inward into a depression.
The mold surface opposite to the rib must be cooled down to reduce the mold temperature there so that the condensation layer is formed faster, and when the condensation layer is thicker, the rigidity is greater and the depression is less likely to occur.
The mold temperature setting can be set from the material manufacturer’s recommended value. Each adjustment can be reduced (or incremented) by 6 ℃ for 10 shots, and after the molding situation is stabilized, further adjustments will be decided based on the results.
Sink mark of injection molded parts caused by too small sprue, runner, or/and gate
If the sprue, runner, or gate is too small, the flow resistance will be increased, and if the injection pressure is not enough, the cavity will not be filled, the melt density will be low, and the chance of denting will be high.
Improper number or location of gates causes sink mark of injection molded parts
No matter whether the number or location of gates is improper, it will make the flow length too long and the flow resistance too large. If the injection pressure is not enough, the cavity cannot be filled, the density of molten rubber is small, and the chance of denting is large.
Sometimes, due to the defect of mold manufacturing, the shrinkage of the outer surface of the injection molded part at the cylindrical (cylinder) position is difficult to solve no matter how to adjust the machine. Even if the problem is solved, the injection molded part is already a full-body batch front.
There are two main reasons for the serious sink marks of the syringe position.
The syringe needle is too short or too thin, making the injection molded parts in the syringe root position of the rubber parts too thick (such as more than 4 mm, while the wall thickness of the other positions of the injection molded parts is only 2 mm), the shrinkage problem is inevitable, and the thicker the more difficult to solve, and even can not be solved by adjusting the machine. This is the case in most of the production.
The wall thickness of the injection parts at the end of the syringe needle is too long (for example, less than 0.3mm), which causes the thermal strength of the plastic parts to be very low.
When the injection parts are out of the mold, the syringe needle is drawn outward, and a vacuum is formed inside the syringe hole, and the atmospheric pressure outside will depress the surface of the injection parts, which is similar to shrinkage.
Therefore, before solving such a shrinkage problem, we should first cut the injection molded part to observe, and find that the location of the injection molded part is too thick, generally not thicker than the wall thickness of the injection molded part, we should lengthen the syringe needle until the shrinkage is OK;
If you find that the shrinkage position is too thin (usually not less than 0.5 mm), you can use a grinding machine to grind the syringe needle short, and the shrinkage problem can be solved.
In addition, spraying some mold release agents on the cylinder can also be used as an auxiliary means to enhance the improvement effect of shrinkage. The release agent can make the syringe pin order, enhance the cooling effect of the location, thus reducing the degree of shrinkage, but also prevent the formation of a vacuum when the syringe is ejected because the release agent will produce a little gas more or less.
What are the reasons for the sink mark of the injection molding machines?
The temperature of the material tube is too high, causing sink mark of injection molded parts
When the temperature of the material tube is too high, the density of melt glue is small, when cooling, the melt glue near the surface of the cavity is first cured into a condensation layer (Frozen Layer), and the volume of plastic shrinkage, the density of melt glue in the center of the cavity is smaller, wait until the central melt glue is also gradually cured, the cavity will be hollowed out, the cavity wall is full of tensile stress.
If the rigidity of the condensation layer is not enough, it will collapse inward and form a depression. If the temperature of the material is lowered, the density of molten glue will be higher and the chance of sinking will be smaller.
Cooling time is not enough to cause sink mark of injection molded parts
Not enough cooling time, the plastic condensation layer is not thick enough to resist the internal melt glue curing shrinkage generated by the tension, forming a dent. Material suppliers can provide the recommended value of cooling time for different plastic and product thicknesses.
Cushion or/and insufficient holding pressure causes shrinkage of injection molded parts
Insufficient holding pressure or holding time, the plastic in the cavity is not filled solidly due to low pressure or insufficient replenishment, the density is low, and the chance of sinkage is high.
Buffer becomes 0, the screw to the bottom, is no longer moving forward, molten rubber cooling, and shrinkage pressure is reduced, but the screw can not increase pressure, resulting in insufficient pressure, and the chance of denting.
The buffer should be at least 3mm to be enough. The holding pressure should be sufficient. The pressure-holding time should be at least 2 seconds.
Non-return valve failure causes sink mark of injection molded parts
The non-return valve prevents the molten rubber in front of the screw in the material tube from flowing back during the injection stage. If the check valve is worn, broken, or improperly located, the melt may slip past the front end of the screw, the gap between the check valve and the material tube, causing the screw to push the bottom out and the cushion to disappear, resulting in a high chance of denting.
Check the check valve from the front end of the screw, and check the contact surface, if there is scorched glue (Burned Plastics) on the surface, use a wire brush (Wire Brush) to remove it; do not use a torch (Torch) to burn off the plastic, because high heat will soften the valve metal, making it accelerate wear.
If the contact surface is found on the carving/nicks, cracks, or pits, the parts with this defect should be replaced.
What are the causes of sink marks of injection molded parts caused by equipment?
① The hopper interrupts the material;
② The hopper neck is partially or completely blocked;
③ Insufficient filling quantity;
④ The operation of the charging control system is not normal;
⑤ The plasticizing capacity of the injection press is too small;
⑥ The injection cycle is abnormal due to the equipment.
What are the reasons for the sink marks of injection molded parts caused by injection molding conditions?
① Injection pressure is too low;
② Too much injection pressure loss in the injection cycle;
③ Injection time is too short;
④ The injection full pressure time is too short;
⑤ Injection rate is too slow;
⑥ Interruption of material flow in the mold cavity;
⑦ Unequal mold filling rate;
⑧ Abnormal injection cycle caused by operating conditions.
What are the causes of the sink marks of injection molded parts caused by temperature?
①Increase the barrel temperature;
②Increase the nozzle temperature;
③ Check the millivolt meter, thermocouple, electric resistance heater (or far-infrared heating device), and heating system;
④ Increase the mold temperature;
⑤ Check the mold temperature control device.
What causes the sink marks of injection molded parts?
① The flow channel is too small;
② The gate is too small;
③ Nozzle hole is too small;
④ Unreasonable gate position;
⑤ Insufficient number of gates;
⑥Cold material cavity is too small;
⑦ Insufficient air venting;
⑧ The injection cycle is abnormal due to the mold;
What are the reasons for the sink marks of injection molded parts caused by materials?
① The liquidity of the material is too poor.
Besides the What Causes Sink Marks in Injection Molded Parts article, you may also be interested in the below articles.
Summary Of 50 Injection Mold Structure Operation Dynamic Diagrams
Auto Parts Stamping Die Design Concept