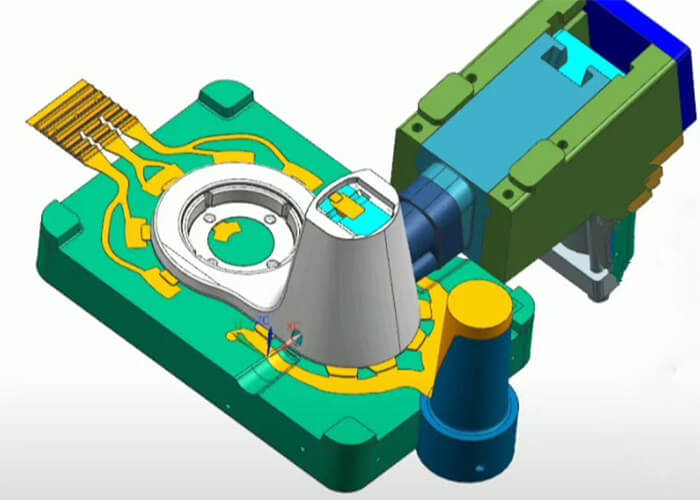
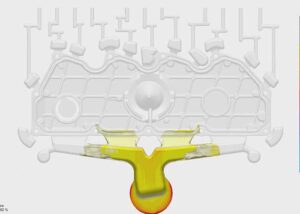
This article talks about what are injection-molded parts and how they form. Enjoy it.
What are injection-molded parts?
Injection-molded parts refer to various injection-molded products produced by injection molding machines, collectively referred to as injection molded parts, including various packaging, parts, etc. It is mainly made of materials such as polyethylene or polypropylene and added with a variety of organic solvents.
Injection-molded parts Introduction
The choice of plastic parts is mainly determined by the type of plastic (thermoplastic or thermosetting), the initial form, and the shape and size of the product. Molding, transfer molding, and injection molding are generally used to make injection molded parts. Laminating, molding, and thermoforming are forming plastics on a flat surface. The above methods can be used in rubber processing.
In addition, there are castings using liquid monomers or polymers as raw materials. Among these methods, extrusion and injection molding are the most used, and they are also the most basic molding methods.
Injection-molded parts Process parameters
The main process parameters of injection molded parts include barrel temperature, melt temperature, mold temperature, and injection pressure.
1. Barrel temperature
The temperature of the melt is very important, and the temperature of the injection cylinder used is only a guideline. The temperature of the melt can be measured at the nozzle or using the air jet method. The temperature setting of the injection cylinder depends on the melt temperature, screw speed, back pressure, injection volume, and injection molding cycle.
If you have no experience in processing a certain grade of plastic, please start with the lowest setting. To facilitate control, the shooting cylinder is divided into zones, but not all are set to the same temperature.
If the operation time is long or the operation is at a high temperature, please set the temperature of the first zone to a lower value, which will prevent the plastic from melting and shunting prematurely.
Before starting the injection molding, make sure that the hydraulic oil, hopper closure, mold, and injection cylinder are all at the correct temperature.
2. Melting temperature
The melt temperature plays a major role in the flow properties of the melt. Since plastics have no specific melting point, the so-called melting point is a temperature range in the molten state. The structure and composition of the plastic molecular chain are different, so the influence on its fluidity is different.
Rigid molecular chains are obviously affected by temperature, such as PC, and PPS, etc., while flexible molecular chains such as PA, PP, PE, etc., the fluidity is not obvious by changing the temperature, so the reasonable temperature of injection molded parts should be adjusted according to different materials.
3. Mold temperature
Some plastic materials require higher mold temperatures due to high crystallization temperature and slow crystallization speed. Some plastic materials require higher temperatures or lower temperatures due to the need to control size and deformation or demolding. For example, a PC generally requires 60 degrees or more.
To achieve a better appearance and improve the fluidity of PPS, the mold temperature sometimes needs to be above 160 degrees. Therefore, the mold temperature has an inestimable effect on improving the appearance, deformation, size, and rubber mold of the product.
4. Injection pressure
Melt overcomes the resistance required for advancement, which directly affects the size, weight, and deformation of the product. Different plastic products require different injection pressures.
For materials such as PE and PP, increasing pressure will significantly improve their fluidity. Injection pressure size determines the density of the product, that is, the appearance of gloss. It has no fixed value, and the more difficult it is to fill the mold, the pressure of the injection molded part will increase.
You may also be interested in the below articles.
Summary Of 50 Injection Mold Structure Operation Dynamic Diagrams
Auto Parts Stamping Die Design Concept