Application and process of a gas-assisted injection molding processing
After the read of this article, you will learn about the application and process of a gas-assisted injection molding process.
The principle of gas-assisted injection molding process
Use high-pressure inert gas (nitrogen) to inject into the molten plastic to form a vacuum section and push the molten material forward, to achieve injection, pressure holding, cooling, and other processes.
Due to the efficient pressure transmission of the gas, the pressure inside the airway can be kept consistent, so the internal stress can be eliminated, the product deformation can be prevented, and the pressure in the mold cavity is greatly reduced, so there is no need for high pressure in the molding process. The clamping force can also reduce product weight and eliminate sink marks.
Gas-assisted injection molding processing equipment
Gas-assisted injection molding processing equipment includes a gas-assisted control unit and a nitrogen generator. It is another system independent of the injection molding machine, and its only interface with the injection molding machine is the injection signal connection line.
After the injection molding machine transmits an injection signal or the screw position to the gas-assisted control unit, it starts a gas injection process. When the next injection process starts, another injection signal is given to start another cycle, and so on. The gas used for gas-assisted injection molding must be inert (usually nitrogen), the maximum pressure of the gas is 35MPa, and the special one can reach 70MPa, and the nitrogen purity is ≥98%.
The gas-assisted control unit is a device that controls the gas injection time and gas injection pressure. It has a multi-group gas circuit design that can simultaneously control the gas-assisted production of multiple injection molding machines. The gas-assisted control unit is equipped with a gas recovery function to reduce gas as much as possible. Consumption.
Gas-assisted injecdtion molding process control
Gas injection parameters
The gas-assisted control unit is a device that controls the gas pressure at each stage. The gas-assisted parameters have only two values: gas injection time (seconds) and gas injection pressure (MPa)
The gas-assisted injection molding process is to inject plastic melt into the mold while injecting high-pressure gas. There is a complex two-phase interaction between the melt and the gas. Therefore, the process parameter control is very important. The control methods of each parameter are as follows:
Injection volume
Gas-assisted injection molding uses the so-called “short shot” method, that is, a certain amount of material (usually 70-95% at a full shot) is injected into the mold cavity, and then gas is injected to achieve a full filling process.
The injection volume of the melt has the greatest relationship with the size of the mold airway and the cavity structure. The larger the airway cross-section, the easier the gas is to penetrate and the higher the hollowing rate, which is suitable for using a larger “short shot rate”. At this time, if too much material is used, it is easy to accumulate molten material and shrink marks will appear in the place where there is much material.
If the material is too little, it will cause blow-through. If the air channel is completely consistent with the flow direction, then it is most conducive to the penetration of gas, and the hollowing rate of the air channel is the largest. Therefore, as far as possible in the mold design, the air channel and the flow direction should be kept consistent.
Injection speed and pressure
In order to ensure that the performance of the product does not appear to be defective, use a higher injection speed as possible to fill the mold cavity as quickly as possible. At this time, the temperature of the melt remains high, which is conducive to gas penetration and mold filling.
The gas maintains a certain pressure after the molten material fills the mold cavity, which is equivalent to the pressure-holding stage in traditional injection molding. Therefore, the gas-assisted injection molding process can generally save the pressure-holding process of the injection molding machine.
However, due to structural reasons, some products still need to use a certain injection pressure to ensure the quality of product performance. But do not use high holding pressure, because too high holding pressure will seal the gas needle, the gas in the cavity cannot be recovered, and it is easy to blow out when opening the mold.
High holding pressure will also hinder the penetration of gas. Increasing the holding pressure of injection may make the product appear more sink marks.
Gas pressure and gas injection speed
The gas pressure has the greatest relationship with the fluidity of the material. Materials with good fluidity (such as PP) use lower gas injection pressure.
The gas pressure is large, easy to penetrate, but easy to blow through; the gas pressure is small, the mold filling may be insufficient, the filling is not full or the product surface has shrink marks; the gas injection speed is high, and the mold cavity can be filled under the condition of high melt temperature.
For molds with long processes or small airways, increasing the air injection speed is conducive to the filling of the melt and can improve the quality of the product surface. However, if the air injection speed is too fast, there may be blow-through, for products with large airways. Will cause surface flow marks and airlines.
Delay
The delay time is the time period from the start of the injection molding machine to the time when the gas-assisted control unit starts to inject gas, which can be understood as the parameter of the synchronization of the anti-mapping glue and the gas injection.
The delay time is short, that is, the gas injection is started when the melt is still at a relatively high temperature, which is obviously conducive to gas penetration and mold filling, but the delay time is too short, the gas is easy to diverge, the hollowing shape is not good, and the hollowing rate is also not enough.
Gas-assisted mold
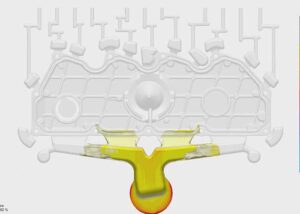
The gas-assisted mold is not much different from the traditional injection mold, only the air intake component (called the air needle) is added, and the design of the air passage is increased. The so-called “airway” can be simply understood as the passage of gas, that is, the part through which the gas flows after entering.
Some of the airways are part of the product, and some are specially designed glue levels for guiding the airflow.
The gas needle is a key part of the gas-assisted mold, which directly affects the stability of the process and product quality. The core part of the air needle is that many small gaps are too large and will be blocked by the melt, and the air output will decrease instead.
The gas-assisted injection molding process
The process of gas-assisted injection molding has four steps
The first step of resin filling: the mold is partially filled with melt.
The second step of gas filling: nitrogen is injected into the hot melt as required. The gas flows at high speed and low pressure. The direction of gas flow is usually the direction of the least resistance.
According to the design, the airway should be placed in a place that is easy to guide the gas to the low-pressure area. The hot melt material at the thick section of the plastic part is replaced by pressure gas is used to fill the plastic with this pressure gas;
The third step of gas pressure maintenance: due to the combined action of the melt and the gas, after the mold is filled, nitrogen is left in the gas flow path of the plastic part, and it has enough pressure to compact the plastic part.
Then the resin cools and shrinks, and the gas presses the resin that has not yet solidified into the gap caused by the shrinkage. Use holding pressure to eliminate sink marks on the surface of plastic parts, and ensure that the mold has a good surface quality in the next molding cycle to form plastic parts with good surface quality;
The fourth step is gas exhaustion: all gases required in the entire process must be exhausted before the mold is opened. If the pressure gas is not discharged in time, the plastic parts will expand or even burst.
You may also be interested in the below articles:
Summary Of 50 Injection Mold Structure Operation Dynamic Diagrams