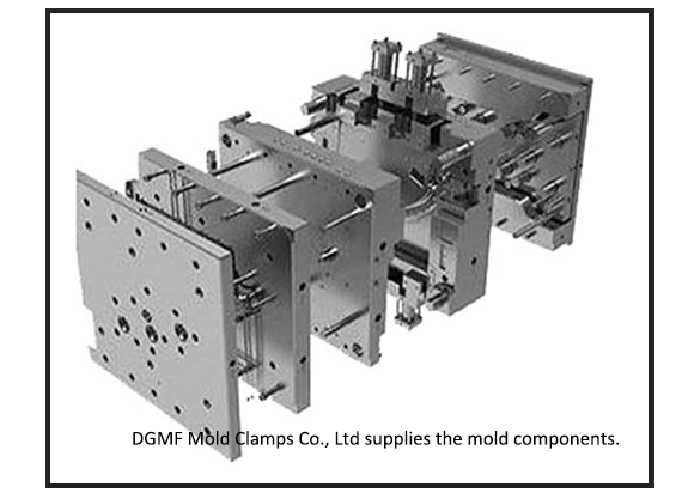
Die-casting mold vs plastic injection mold, what is the difference?
What is the difference between die casting mold and plastic mold?
- The injection molding pressure of the die-casting mold is larger, so the template needs to be relatively thick to prevent deformation
- The gate of the die-casting mold is different from the plastic injection mold, and the high pressure of the split cone to decompose the flow needs to be done
- Die core of die casting mold does not need to be quenched, because the temperature in the mold cavity exceeds 700 degrees during die casting.
It is equivalent to quenching once. The die-cast mold cavity will become harder and harder. The general plastic injection mold should be quenched to above HRC52.
- The general cavity of the die-casting mold should be nitrided to prevent the alloy from sticking to the mold cavity.
- Generally, the die-casting mold is relatively corroded, and the outer surface is generally bluish.
- Compared with the plastic injection mold, the matching clearance of the movable matching part of the die casting mold (such as the core pulling slider) is larger,
Because the high temperature in the die casting process will cause thermal expansion. If the gap is too small, it will cause the mold to jam.
- The requirements of the parting surface of the die-casting mold are higher because the fluidity of the alloy is much better than that of the plastic.
It is very dangerous for the high-temperature and high-pressure stream to fly out of the parting surface
- The injection mold generally depends on the thimble and the parting surface can be exhausted. The die casting mold must have an exhaust slot and a slag collection bag (collecting cold material head);
- The molding is inconsistent, the injection speed of the die-casting mold is fast, and the injection pressure is one section. The plastic mold is usually injected into several sections to maintain the pressure.
- The die-casting mold is opened with two plate molds at one time, and the product structure of different plastic molds is different.
Plate molds are common, and the number and order of mold openings are compatible with the mold structure. Die-casting molds usually do not use a square ejector pin, sleeve pin, guide pins (high temperature and good fluidity of the solution) are easy to get stuck, resulting in unstable injection mold production.
The main difference between the die casting mold and plastic mold is that on the feed sprue bushing, the plastic mold sprue bushings are slender tapered feed ports, the diameter of the feed port is relatively small, and the die casting mold is relatively large. The diameter of the tapered feed port of the center feed is much larger than the feed port of the plastic mold.
Another feed port is a straight round sleeve with a diameter of 30 to 40 mm, which is a structure not found in plastic injection molds. In addition, plastic injection molds and die-casting molds use different steels; plastic molds generally use 45# steel, T8, T10, and other steels, while die-casting molds mainly use heat-resistant steels such as 3Cr2W8V.
You may also be interested in the below articles:
Summary Of 50 Injection Mold Structure Operation Dynamic Diagrams