After the read of How to Determine the Air Vents of Thin-Walled Molds article, you will learn about:
- Air vents method
- Design method
- Design size of air venting groove
- Conclusion
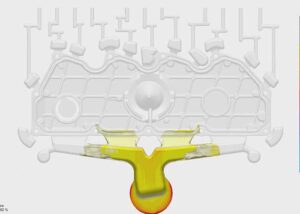
The thinner the product, the farther away from the gate, the opening of the mold air vent groove is particularly important. In addition, for small parts or precision parts, the opening of the venting groove should also be paid attention to, because it can not only avoid surface burns and insufficient injection volume but also eliminate various defects of the product and reduce mold pollution.
The function of the mold air vent groove mainly has two points, one is to remove the air in the mold cavity when the molten material is injected; the other is to remove various gases generated during the heating process of the material.
So, what are sufficient air vents in the cavity? Generally speaking, if the melt is injected at the highest injection rate, but no focal spots are left on the product, it can be considered that the air vents in the cavity are sufficient.
1. Air vents method
There are many ways to vent the mold cavity, but each method must be guaranteed, the size of the air vent slot should be designed to prevent the material from overflowing into the slot while the air venting slot is vented; secondly, it should prevent blockage.
Therefore, measuring from the inner surface of the mold cavity to the outer edge of the mold cavity, the height of the venting groove above 6-12mm should be about 0.25-0.4mm.
In addition, too many air vent grooves are harmful. Because of the clamping pressure acting on the parting surface of the mold cavity without opening the vent groove is very large, it is easy to cause cold flow or cracking of the mold cavity material, which is very dangerous.
In addition to venting the mold cavity on the parting surface, it is also possible to achieve the purpose of venting by arranging the venting groove at the end of the material flow of the pouring system and leaving a gap around the ejector rod.
If the selection of the depth, width, and position of the opening is not appropriate, the flash burr produced will affect the appearance and accuracy of the product. Therefore, the size of the above gap is limited to prevent flash around the ejector rod.
Special attention should be paid, when a part such as gear is vented, even the smallest flash may be undesirable. It is best to use the following method to vent the gear part.
(1) Completely remove the gas in the flow channel;
(2) Shot peening the mating surface of the parting surface with silicon carbide abrasive with a particle size of 200.
In addition, the opening of the air vent groove at the end of the material flow of the pouring system mainly refers to the air vent groove at the end of the runner. Its width should be equal to the width of the runner, and the height varies depending on the material.
2. Design method
For product molds with complex geometries, it is best to determine the opening of the vent slot after several mold trials. The biggest disadvantage of the overall structure of the mold structure design is the poor air vents.
For the integral cavity core, there are the following air venting methods:
(1) Use the groove or insert installation position of the cavity;
(2) Use the side insert seams;
(3) Partially made into a spiral shape;
(4) Install a slotted slat core and open a craft hole in the longitudinal position.
When the air venting is extremely difficult, the mosaic structure is adopted. If the dead corners of some molds are not easy to open the air venting groove.
First of all, without affecting the appearance and accuracy of the product, the mold should be appropriately changed to inlay processing. This will not only help to process the mold air venting groove but sometimes also improve the original Difficulty in processing and easy maintenance.
3. Design size of air venting groove
The venting of thermoset materials is more important than that of thermoplastic materials.
First of all, the runners in front of the gate should be vented. The width of the mold air venting slot should be equal to the width of the runner and the height is 0.12mm.
All sides of the mold cavity should be vented. The mold air venting slots should be 25mm apart, 6.5mm wide, and 0.075-0.16mm high, depending on the fluidity of the material. Softer materials should take lower values.
The ejector rod should be enlarged as much as possible, and in most cases, 3-4 flat surfaces with a height of 0.05mm should be ground on the cylindrical surface of the ejector rod, and the wear scar direction should be along the length of the ejector rod.
Grinding should be carried out with a fine-grained grinding wheel. The end face of the ejector rod should be ground with a chamfer of 0.12mm so that if there is a flash formed, it will adhere to the workpiece.
4. Conclusion
Properly opening the vent groove can greatly reduce the injection pressure, injection time, holding time and clamping pressure, so that the molding of plastic parts can be changed from difficult to easy, thereby improving production efficiency, reducing production costs, and reducing machine energy consumption.
In fact, it is not necessary to exhaust air vents through the exhaust groove. There are several other ways to air venting.
(1) Mold air vents from the air venting slot
For molds for forming large and medium-sized plastic parts, a large amount of gas needs to be removed, and an air venting groove is usually provided, which is usually opened on the side of the concave mold on the parting surface.
The location of the mold air venting slot is better at the end of the melt flow, and the size of the mold air venting slot is based on the principle that the gas can be smoothly discharged without overflow. The width of the mold air vent groove is generally about 3-5mm, the depth is less than 0.05mm, and the length is generally 0.7-1.0mm.
(2) Parting surface air vents
For small molds, the parting surface gap can be used to vent, but the parting surface must be at the end of the melt flow.
(3) Air vent the gap of the mosaic
For combined dies or cavities, the split gap can be used to vent.
(4) Venting the push rod gap
Use the matching clearance between the pushrod and the template or core to the air vent, or intentionally increase the clearance between the pushrod and the template.
(5) Air venting of powder unsintered alloy block
The powder unsintered alloy is a material sintered with a spherical particle alloy, which has poor strength, but has a loose texture and allows gas to pass through. Placing a piece of such alloy in the part that needs to be vented can meet the requirements of venting, but the diameter of the bottom vent hole should not be too large to prevent it from being squeezed and deformed by the pressure of the cavity.
(6) Mold air vents from venting well
On the outside of the plastic melt confluence, a cavity is provided to allow gas to be discharged into it, and a good exhaust effect can also be obtained.
(7) Mandatory air vents
Set the mold air venting rod in the part where the gas is enclosed. This method has a good mold air vent effect, but it will leave traces of the rod on the plastic part, so the mold air venting rod should be located in a hidden place of the plastic part.
You may also be interested in the below articles:
You may also be interested in the below articles:
6 Polishing Methods For Plastic Injection Molds
10 Plastic Injection Molding Methods
What Is The Difference Between Blow Molding And Injection Molding?