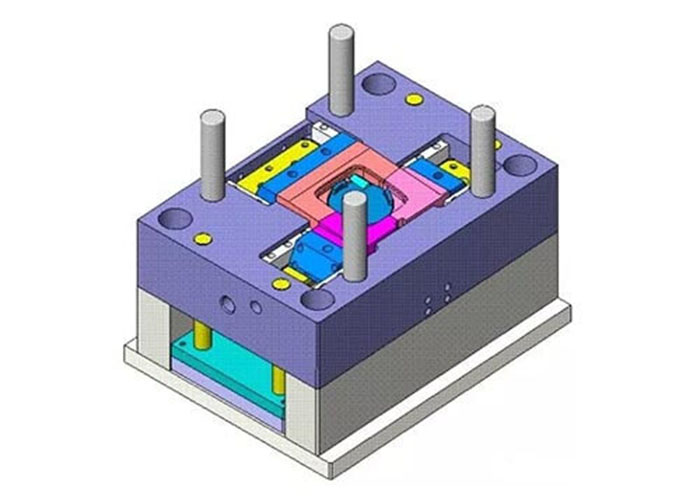
After reading the basic requirements for plastic injection molded part design article. You will know the plastic injection molded part design basic requirements.
Why requirements for plastic injection molded part design are needed?
Unreasonable design of plastic injection molded parts often results in some inherent defects in the product.
For example, the structure of the parts is unreasonable, the parts use too much material, etc. Here are a series of basic requirements for plastic injection molded parts design for reference.
What are the basic requirements for plastic injection molded part design?
1. The basic content of plastic injection molded parts
Three-dimensional space content, geometric structure, size, and accuracy.
The content, marks, symbols, text, surface patterns, graphics, and roughness of the surface of the plastic part.
Static and dynamic performance, mechanical, physical, and chemical properties.
Environment and ergonomics.
The choice of plastic.
Cost and price.
The feasibility and economic efficiency of forming molds and forming methods.
2. Geometric structure and dimensional accuracy
The structure includes the design of the internal structure and external structure.
1.1. Shape
The shape of the plastic part should be as good as possible to ensure the principle of forming.
1.2. Demolding slope
Due to the shrinkage of the plastic part after cooling, the plastic part will tightly wrap the mold core and the convex part in the cavity (mainly overwrap core), in order to facilitate the removal of the plastic part and prevent demolding When designing plastic parts, the inner and outer surfaces should have sufficient demoulding inclination along the demolding direction.
When designing, pay attention to the following aspects:
When compressing and forming larger plastic parts, the demolding slope of the inner surface is required to be greater than that of the outer surface.
The common demolding slope value is 1°~1.5°, and it can be as small as 0.5°.
For plastic parts with a small height, the draft angle is not required.
1.3. Wall thickness
The wall thickness of the plastic part is related to the use of requirements and process requirements.
In plastic molding, the wall thickness is too small, and the flow of molten plastic in the mold cavity is relatively large.
If the wall thickness is too large, it will cause too much material, increase the cost, and bring difficulties to the molding process. Air bubbles, shrinkage holes, dents, warping, etc. will also be generated on the plastic parts, which will affect the appearance of the product.
In the molding process, the wall thickness of each part of the plastic part is required to be as uniform as possible.
1.4. Reinforcing ribs
It is a method often used in plastic parts to increase the strength of plastic parts.
Its advantages:
Make the wall thickness of the plastic parts uniform, which not only saves materials, but also improves the strength, and can also avoid appearance defects in the plastic parts.
Increase the rigidity of plastic parts.
The reinforcing ribs along the direction of material flow can also reduce the negative force of plastic filling.
Design requirements for stiffeners:
In order to enhance the strength and rigidity of the plastic parts, the reinforcing ribs should be designed to be shorter and more.
The center distance between the ribs should be greater than twice the wall thickness.
For thin-walled plastic parts, it can also be designed into a spherical or arched surface shape.
1.5. Supporting surface
It is unreasonable to use the entire bottom surface of the plastic part as the supporting surface. The frame support or foot support is usually used.
1.6. Fillet
Except that sharp corners must be used on plastic parts, all other corners should adopt arc transition, because the sharp corners are prone to stress concentration and affect the strength of plastic parts.
There are two main advantages of using rounded corners
Avoid stress concentration, and improve the strength and appearance of plastic parts.
The mold will not crack due to stress concentration during quenching and use.
1.7. Hole
The hole on the plastic part is formed by the core of the mold. The following points should be paid attention to in the design.
The hole should be set in a place that is not easy to weaken the strength of the plastic part.
There should be sufficient distance between the holes and between the holes and the edge (generally it should be larger than the hole diameter).
For blind holes, the depth of the hole shall not be greater than 4 times the diameter of the hole during extrusion or injection molding.
1.8. Hinge design
The design of the hinge mainly has the following points
For the plastic part itself, the intermediate film should be thinner with a small wall thickness, and the film should be thicker for the larger wall, but not more than 0.5mm.
The thickness of the hinge part should be uniform.
When molding, the plastic must flow from the side of the plastic part through the intermediate film to the other side, and bend several times immediately after demolding.
1.9. Anti-rotation convex and concave
The anti-rotation convex and concave design on the plastic part is generally for the convenience of gripping and easy screwing out after the plastic part is formed. In the design, attention should be paid to: the convex and concave grain direction is consistent with the demolding direction and the mold is easy to process.
1.10. Thread
The thread on the plastic part can be formed directly during molding, or it can be machined after molding.
The diameter of the external thread of the molded thread should not be less than 4mm, the diameter of the internal thread should not be less than 2mm, and the accuracy should not be higher than class 3.
To prevent the outermost thread of the screw hole on the plastic part from cracking or deforming, there should be a stepped hole with a depth of 0.2~0.8mm at the beginning of the hole, and the end of the thread should not extend to the bottom surface.
1.11. Gears
The dimensions of each part of the gear are as follows:
A-1. The minimum rim width is 3 times the tooth height.
A-2. The thickness of the web should be equal to or less than the thickness of the rim.
A-3. The thickness of the wheel shell should be equal to or greater than the thickness of the wheel rim.
A-4. The minimum outer diameter of the wheel housing should be 1.5 to 3 times the diameter of the shaft.
A-5. The length of the wheel housing should be equivalent to the shaft diameter.
When designing gears, you should also pay attention to
B-1. Try to avoid sudden changes in cross-section.
B-2. Increase the radius of fillet and arc transition as much as possible.
B-3. As far as possible, the shaft and the hole should not adopt an interference fit, but a transition fit can be adopted.
1.12. Inserts
The purpose of the insert:
Increase the local strength, hardness, wear resistance, conductivity, and magnetic permeability of plastic parts.
Stability of the size and shape of plasticized parts to improve accuracy.
Reduce the consumption of plastics and meet other requirements.
Surface form of the insert
Rhombus knurling, straight knurling, hexagon, cut, perforation, bending, offset, etc.
3. Design requirements for inserts
3.1. In order to prevent stress cracking of plastic parts, the plastic layer around the insert should have sufficient thickness, and the structure of the insert itself should not have sharp corners.
3.2. Plastic parts with inserts on one side, due to uneven shrinkage on both sides, cause great internal stress, which will cause the plastic parts to bend or break.
3.3. In order to prevent displacement or deformation of the insert due to plastic flow pressure, the insert should be firmly fixed in the mold. Welcome to follow the WeChat official account of Micro Injection Molding.
3.4. The design of inserts should try to use non-through holes or non-through screw holes.
3.5. To avoid bulging, sleeve inserts should not be placed on the surface or near the edge of the plastic part.
3.6. In order to improve the stability of the insert in the mold, when conditions permit, there should be a flange on the insert, and it should be recessed or raised by 1.5~2mm.
3.7. When the free extension length of the insert exceeds 2 times the diameter of the support of the insert, the insert perpendicular to the compression molding direction should have a supporting column.
3.8. When the insert is a screw, the mating part of the polished rod part and the mold should have a clearance fit with IT9 accuracy.
3.9. In order to connect the insert and the plastic part firmly, the surface of the insert should have a stop part to prevent the insert from moving.
You may also be interested in the below articles:
Summary Of 50 Injection Mold Structure Operation Dynamic Diagrams