After reading 10 Plastic Injection Molding Methods article. You will know the 10 common plastic Injection molding methods.
Plastic products are made of a mixture of synthetic resin and various additives as raw materials, using injection, extrusion, pressing, pouring, and other methods. While plastic products are being molded, they also obtain the final performance, so plastic molding is a key production process.
10 common plastic Injection molding methods
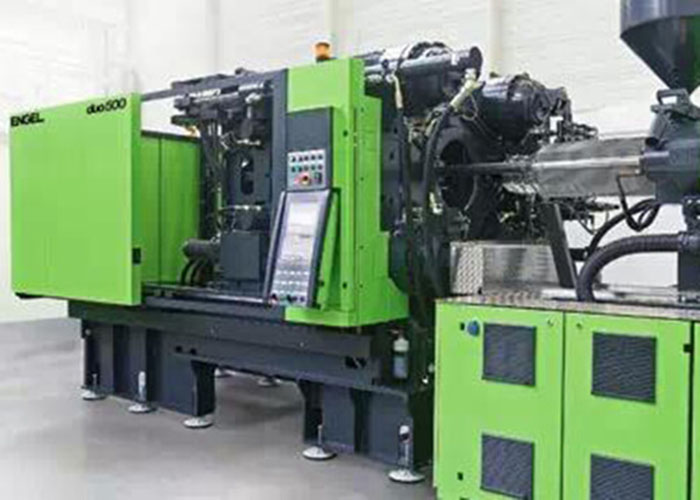
Plastic Injection molding method 1. Injection molding
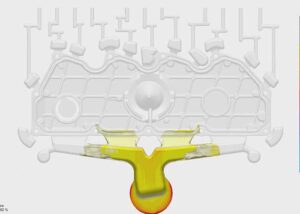
Injection molding is a method of using an injection machine to quickly inject molten plastic into a mold and solidify to obtain various plastic products.
Injection molding is a method in which plastic is first heated and melted in the heating barrel of the injection molding machine, and then the melt is pushed into the cavity of a closed mold by a reciprocating screw.
It can not only produce high-precision and high-quality products under high productivity but also has a large variety of plastics that can be processed, large output (about 1/3 of the total amount of plastics), and wide use. Therefore, injection molding is one of the important molding methods of plastic processing.
Plastic Injection molding method 2. Extrusion molding
Extrusion molding is a process in which plasticized plastics are continuously extruded into the mold by means of screw rotation and pressure, and when passing through a certain shape of the die, a plastic profile suitable for the shape of the die is obtained.
Extrusion molding is a method in which the plastic is continuously passed through the die in a flowing state by heating and pressing in an extruder.
It is generally used for the molding of sheets, pipes, monofilaments, flat wires, films, wires, and cables, etc., with a wide range of uses and high output. Therefore, it is one of the important molding methods in plastics.
Plastic Injection molding method 3. Foam molding
Foam molding refers to the addition of suitable foaming agents to foam materials to produce porous or foamed products. The foamed products have low relative density, high specific strength, low raw material consumption, sound insulation, and heat insulation. Foam materials include PVC, PE, and PS, etc.
Products include film, sheet, pipe, and profile, etc. Foaming can be divided into chemical foaming and physical foaming.
Plastic Injection molding method 4. Blow molding
Blow molding (expanded film) (or hollow blow molding) refers to a molding method in which the hot thermoplastic parison or sheet in a closed mold is inflated into a hollow product by means of fluid (compressed air) pressure.
Plastic containers produced by this method. Such as various bottles, square, round or flat barrels, gasoline tanks, etc. have been widely used, and newly developed various industrial parts and daily products, such as double-walled box-shaped products, L-ring large drum.
Stacking board, Surfboard, Seatback, and desk, as well as automobile front spoiler, belt cover, instrument panel, air-conditioning ventilation pipe, etc., which have been applied in practice.
The processed materials from daily-use plastics to engineering plastics, blow molding has become one of the important molding methods in plastic processing.
But the basic steps of the blow molding process are:
4.1. Melting materials.
4.2. The molten resin is formed into a tube or parison.
4.3. Melt the hollow parison in the blow mold.
4.4. Inflate the parison in the mold.
4.5. Cool blow-molded products.
4.6. Take out the product from the mold.
4.7. Trimming
Plastic Injection molding method 5. Injection blow molding
Injection blow molding (belonging to the secondary processing of plastics) is a processing method in which hollow plastic parisons are blown and deformed by means of compressed air, and the plastic parts are obtained after cooling and shaping.
Injection blow molding is a blow molding method. First, plastic is made into a bottomed parison by injection molding, and then it is moved to a blow mold to blow into a hollow product.
This method can be used to produce packaging containers for daily necessities, cosmetics, medicine, food, etc., but its volume should not exceed 1L. Commonly used plastics include polyethylene, polystyrene, and polyvinyl chloride.
Plastic Injection molding method 6. Extrusion blow molding
Extrusion blow molding is a blow molding method. It is different from injection blow molding. Its parison is made by extrusion.
Plastic Injection molding method 7. Stretch blow molding
Stretch blow molding is a blow molding method. It uses extrusion, injection molding, and other methods to make a parison. Then the parison is heated to the stretching temperature. Through the internal (such as mandrel) or external (For example, the mechanical force of the clamp) is used for longitudinal stretching. At the same time or later, it is expanded by compressed air for transverse stretching.
Plastic Injection molding method 8. Compression molding
Compression molding is to add solid pellets or prefabricated pieces into the mold and use heating and pressure to soften and melt and under pressure The method of filling the mold cavity to obtain plastic parts after curing.
Plastic Injection molding method 9. Casting
The casting of plastic is similar to the casting of metal. That is, the polymer material or monomer material in the flowing state is injected into a specific mold, and under certain conditions, it is reacted, cured, and formed into a processing method of plastic parts consistent with the mold cavity.
Plastic Injection molding method 10. Gas-assisted forming
Gas-assisted injection molding (referred to as gas-assisted molding) is a new method in the field of plastic processing. Divided into hollow forming, short shot, and full shot.
The main component of plastic is a resin
Resin refers to a polymer compound that has not been mixed with various additives. The term resin was originally named for the lipids secreted by plants and animals, such as rosin and shellac. The resin accounts for about 40% to 100% of the total weight of the plastic.
The basic properties of plastics are mainly determined by the nature of the resin, but additives also play an important role. Some plastics are basically composed of synthetic resins, with no or little additives, such as plexiglass and polystyrene.
You may also be interested in the below articles:
Summary Of 50 Injection Mold Structure Operation Dynamic Diagrams